Key Takeaways
- PCB assembly (PCBA) is the process of mounting and soldering electronic components onto a bare printed circuit board, making it functional for use in modern electronic devices.
- The assembly process involves crucial steps such as solder paste application, precise component placement, soldering (via surface mount and through-hole techniques), and rigorous quality inspections.
- Key components of a PCBA include the bare PCB board, electronic parts like resistors and chips, and high-quality soldering materials, all contributing to circuit reliability.
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) are the primary assembly methods, each suited for different applications, component sizes, and durability requirements.
- PCB assemblies are essential for the compactness, reliability, and performance of electronics in industries such as consumer devices, healthcare, aerospace, and industrial automation.
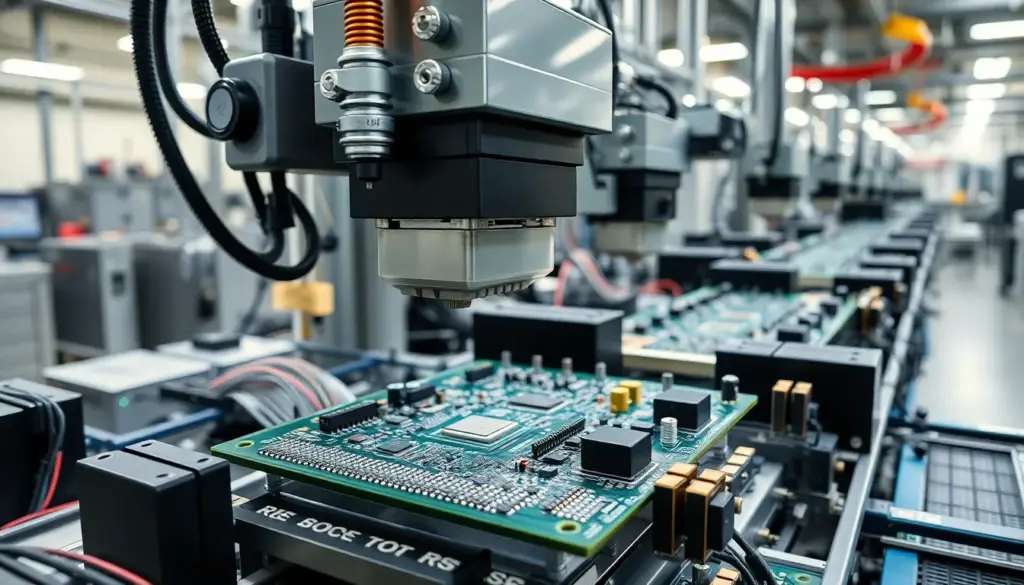
PCB assembly (PCBA) is the process of mounting and soldering electronic components like integrated circuits, resistors, and capacitors onto bare printed circuit boards, creating functional circuits for electronic devices. The assembly process involves solder paste application, precise component placement using automated pick-and-place machines, soldering through Surface Mount Technology (SMT) or Through-Hole Technology (THT), and rigorous quality inspections including automated optical inspection and electrical testing. Key components include bare PCB boards, electronic parts, and high-quality soldering materials, all contributing to circuit reliability and performance. For comprehensive PCB assembly services, pcb assembly manufacturer providers like WellPCB offer turnkey solutions including rapid prototyping, multilayer boards, automated assembly processes, and quality assurance meeting international standards for industries ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace and medical devices.
Understanding What Is a PCB Assembly
A PCB assembly, often called PCBA, is the complete board produced after mounting electronic components like integrated circuits, resistors, capacitors, and connectors onto a finished bare printed circuit board. This process includes soldering components to precisely mapped pads or through-holes using automated machines or manual techniques. PCB assemblies form the functional backbone of electronics including computers, smartphones, medical monitors, and automotive control units.
Manufacturing a PCB assembly involves several steps, typically starting with board fabrication, then surface mounting or through-hole soldering, automated optical inspection, and electrical testing. Factories like WellPCB in China use high-speed pick-and-place machines, reflow or wave soldering, and X-ray inspections for quality and reliability. Quality assurance confirms each assembly meets client specifications, which is essential for critical industries.
PCB assemblies differ by application, with single-sided, double-sided, or multilayer board types created to match custom requirement profiles for performance, size, and complexity. WellPCB offers rapid prototyping, small batch production, and high-volume PCB assembly for global clients, supporting everything from industrial machinery to IoT sensors. Accurate component placement and soldering ensure long operational life and product safety.
Key Components Involved in PCB Assembly
PCB assembly relies on combining specific materials and parts to ensure optimal circuit board function. Each component type impacts the assembly process and the finished product’s reliability.
Bare PCB Boards
Bare PCB boards act as the structural foundation for component assembly. Fabricators produce these boards from insulating substrates like fiberglass or epoxy resin, layering copper to create conductive traces according to engineered circuit layouts (IPC-6012 standard). At WellPCB in China, automated PCB manufacturing ensures precise trace definition for formats ranging from single-sided to multilayer boards. Specialized board types, such as flexible or high-frequency PCBs, are available for applications needing unique electrical or mechanical properties. The bare board must meet exacting tolerances to support defect-free component mounting and dependable circuit connections.
Electronic Components
Electronic components enable the PCB to perform designed electrical functions. Component types—such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, integrated circuits, and connectors—are specified on the bill of materials for each assembly. Engineers select parts based on voltage, current, and size constraints set by the application. For example, microcontrollers, power MOSFETs, and communication modules serve common roles in IoT sensors and industrial controllers manufactured by WellPCB. Placement accuracy, achieved through automated pick-and-place machines, directly affects board performance and failure rates, especially with surface mount packages or densely routed multilayer boards.
Soldering Materials
Soldering materials bond electronic components to PCB pads during assembly. Most production assemblies use lead-free solder paste composed of tin-silver-copper alloys, meeting RoHS requirements enforced since 2006 in the EU and similar global markets. Solder paste includes flux and binder for stable stencil printing and strong adhesion. In reflow soldering, temperature-controlled ovens melt the paste and form reliable joints. Through-hole assemblies may use wave soldering, in which molten solder covers exposed leads underneath the board. WellPCB uses AOI and X-ray inspection to validate solder joint quality and prevent manufacturing defects, ensuring assemblies meet IPC-A-610 standards.
The PCB Assembly Process Explained

PCB assembly transforms a bare circuit board into a functional part by connecting components using precise manufacturing steps. WellPCB in China applies standardized production for both prototyping and high-volume orders.
Solder Paste Application
Solder paste application prepares the board for component mounting. Technicians apply a mixture of powdered solder alloy and flux through a stainless-steel stencil onto the copper pads of the PCB. Accurate stencil alignment ensures solder paste is only deposited where surface-mount devices will go. In high-throughput lines at WellPCB, automated printers keep paste volume and placement consistent, reducing the risk of solder defects. Quality control teams inspect the applied paste after each board passes through the printer to confirm correct coverage and thickness.
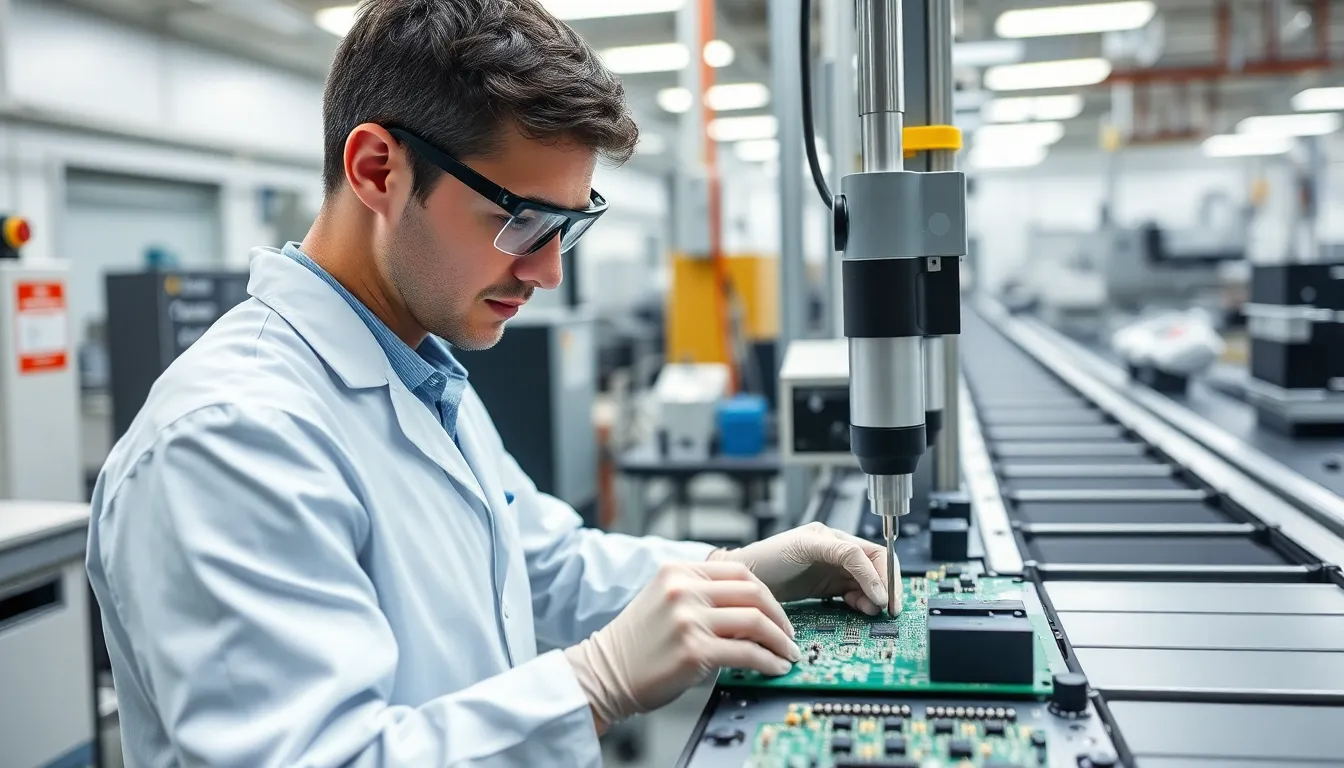
Component Placement
Component placement aligns all board parts before soldering. Automated pick-and-place machines position resistors, capacitors, chips, and connectors on the solder-pasted pads with sub-millimeter precision. Pick-and-place vision systems verify orientation and location in real time. In WellPCB’s facilities, conveyer-driven lines allow rapid head placement, supporting strict positioning tolerances for double-sided and multilayer assemblies. Operators manually place odd-shaped or large components if needed, ensuring every board matches design specifications for performance and durability.
Soldering and Inspection
Soldering and inspection finalize and evaluate each PCBA. For SMT assemblies, reflow ovens heat the board, melting the solder paste and securing parts to the copper pads as the paste solidifies during cooling. Through-hole parts run through wave soldering, where molten solder contacts every pin and pad simultaneously. WellPCB’s assembly lines deploy automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray analysis for hidden joints, and functional testing. Boards failing visual, AOI, or in-circuit tests undergo rework, ensuring all outgoing assemblies meet IPC and customer quality standards.
Types of PCB Assembly Techniques
PCB assembly techniques determine how electronic components connect to printed circuit boards, directly affecting performance, size, durability, and production time. WellPCB, a leading China-based manufacturer, supports both core methods, enabling tailored assembly for consumer electronics and industrial solutions.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
Surface Mount Technology places electronic components, called SMDs, directly onto the PCB surface without drilling holes. Automated machines like pick-and-place systems align and secure parts with notable speed, followed by reflow ovens that heat solder paste to bond components. SMT supports component placement on both PCB sides, high-density layouts, and compact device designs. Examples include smartphones, wearables, and network devices. SMT is suitable for mass production due to minimal manual labor requirements and supports quick turnaround for prototyping and high-volume runs at WellPCB. SMT can place up to 50,000 components per hour, optimizing costs for large-scale products.
Through-Hole Technology (THT)
Through-Hole Technology involves inserting component leads into pre-drilled PCB holes, then soldering these on the opposite side using wave or manual techniques. THT excels in creating robust mechanical bonds, making it suitable for connectors, transformers, and components exposed to physical or thermal stress. Applications include automotive engine controls, industrial machinery, and power supplies. THT accommodates larger components that need reinforced anchoring, but assembly is slower due to manual intervention and limited automation. WellPCB offers THT services for both low-volume prototypes and critical, high-reliability products. THT keeps long-term stability for devices subject to shock or vibration, meeting international reliability standards.
Importance of PCB Assembly in Modern Electronics
PCB assembly gives electronic circuits the ability to perform in modern devices by joining components like ICs, resistors, and capacitors on a bare board. Miniaturization and high-density integration allow manufacturers to pack thousands of components onto small form factors used in smartphones, medical monitors, and IoT devices. Consistent soldering and automated placement—standard in facilities like WellPCB in China—produce reliable high-volume assemblies required for aerospace, healthcare, and industrial automation.
Manufacturers achieve tight process control with automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray analysis, and in-circuit testing. These methods detect faults such as solder bridges, missing components, or poor electrical connections before products reach the field. Table 1 shows application sectors where PCB assembly impacts system reliability and device miniaturization.
| Sector | Examples | Impact of PCB Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer | Smartphones, tablets | Compact design, mass production |
| Healthcare | Medical diagnostics, wearables | Precise function, low failure rate |
| Aerospace | Avionics, communications | Long life, harsh environment |
| Industrial | Automation controllers, sensors | High reliability, fast turnaround |
WellPCB supports global clients with complete PCB assembly solutions, including prototyping, multilayer boards, lead-free soldering, and tailored quality controls designed for demanding performance and stringent safety requirements.
About WellPCB
WellPCB, with locations in Los Angeles, USA, Cavite, Philippines, and Shijiazhuang, China, is a leading provider of PCB manufacturing and assembly services, offering solutions such as turnkey PCB assembly, PCB design services, and rapid prototyping.
Under the leadership of Director of Sales and Marketing, and Co-founder Hommer Zhao, WellPCB delivers high-quality PCB solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of industries such as electronics, telecommunications, and automotive. With a focus on precision engineering and reliability, WellPCB is committed to bringing your PCB concepts to life with advanced technology and efficient processes.
Contact:
Hommer Zhao, Director of Sales and Marketing, Co-founder
Phone: (424) 842-2783
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.wellpcb.com
Location:
- USA: 3826 Medford St, Los Angeles, CA 90063
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a PCB assembly (PCBA)?
A PCB assembly (PCBA) is a finished printed circuit board with electronic components—such as chips, resistors, and capacitors—soldered onto it. This transforms the bare board into a functional part that powers electronic devices.
Why are PCB assemblies important in modern electronics?
PCB assemblies are essential because they connect and support all components inside electronic devices, making reliable operation possible. They enable the miniaturization, performance, and durability needed in everything from smartphones to medical equipment.
What is the difference between SMT and THT in PCB assembly?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) places components directly onto the PCB surface, ideal for compact, high-volume designs. Through-Hole Technology (THT) inserts component leads through drilled holes, providing stronger mechanical bonds for more robust applications.
How are components placed on a PCB during assembly?
Automated machines, called pick-and-place, position most components with high precision. Some large or uniquely shaped parts may be placed manually before being soldered in place during the assembly process.
What quality control measures are used in PCB assembly?
PCB assembly quality is ensured by automated optical inspection, X-ray validation, and electrical or functional testing. These checks identify placement errors, faulty solder joints, or other defects before products ship.
Can PCB assemblies be customized for different applications?
Yes, PCB assemblies can be tailored to meet specific needs. Options include single-sided, double-sided, or multilayer boards, and specialized types like flexible or high-frequency PCBs, depending on the device requirements.
What industries rely on PCB assemblies?
PCB assemblies are crucial in consumer electronics, industrial machinery, medical devices, IoT sensors, aerospace, and more—supporting innovation and reliability in diverse sectors.
Why is soldering important in PCB assembly?
Soldering bonds electronic components to the PCB, ensuring strong electrical connections and mechanical stability. High-quality soldering is vital for the board’s reliability and long operational life.
What materials are used in PCB assembly?
Key materials include the bare PCB (made of insulating substrate and copper), electronic components (such as ICs, resistors), and soldering materials (usually lead-free solder paste) to attach components securely.
How does PCB assembly enhance electronic device performance?
Precise assembly enables high-density layouts and reliable connections, supporting device miniaturization, consistent performance, and the longevity needed in advanced electronics across many industries.